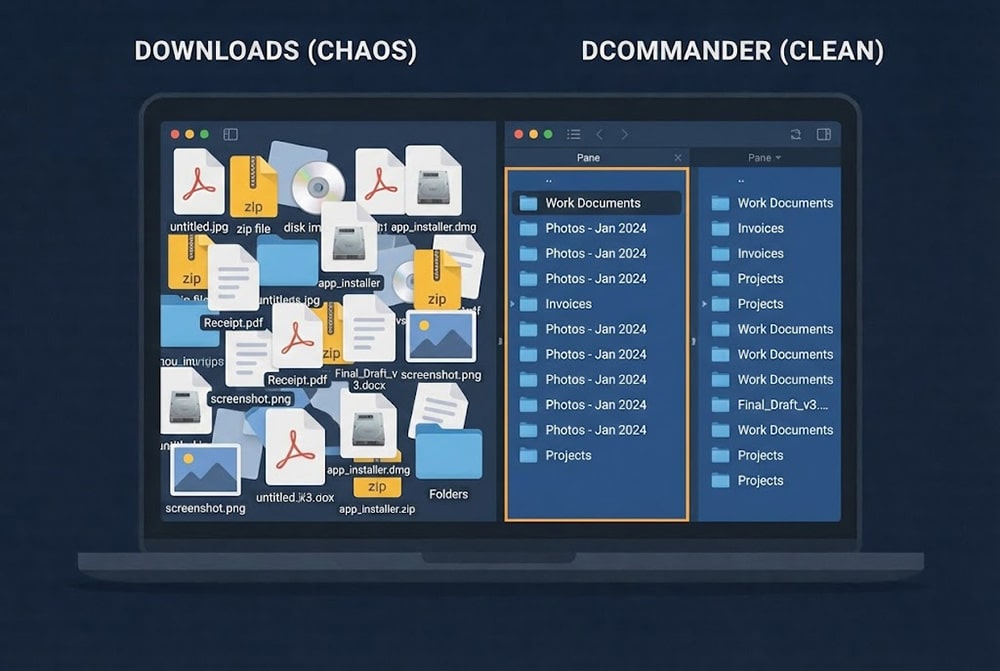
For most users, the attempt to organize downloads folder mac storage is a constant battle…
How to Mirror Folder Mac to External Drive (No Time Machine)
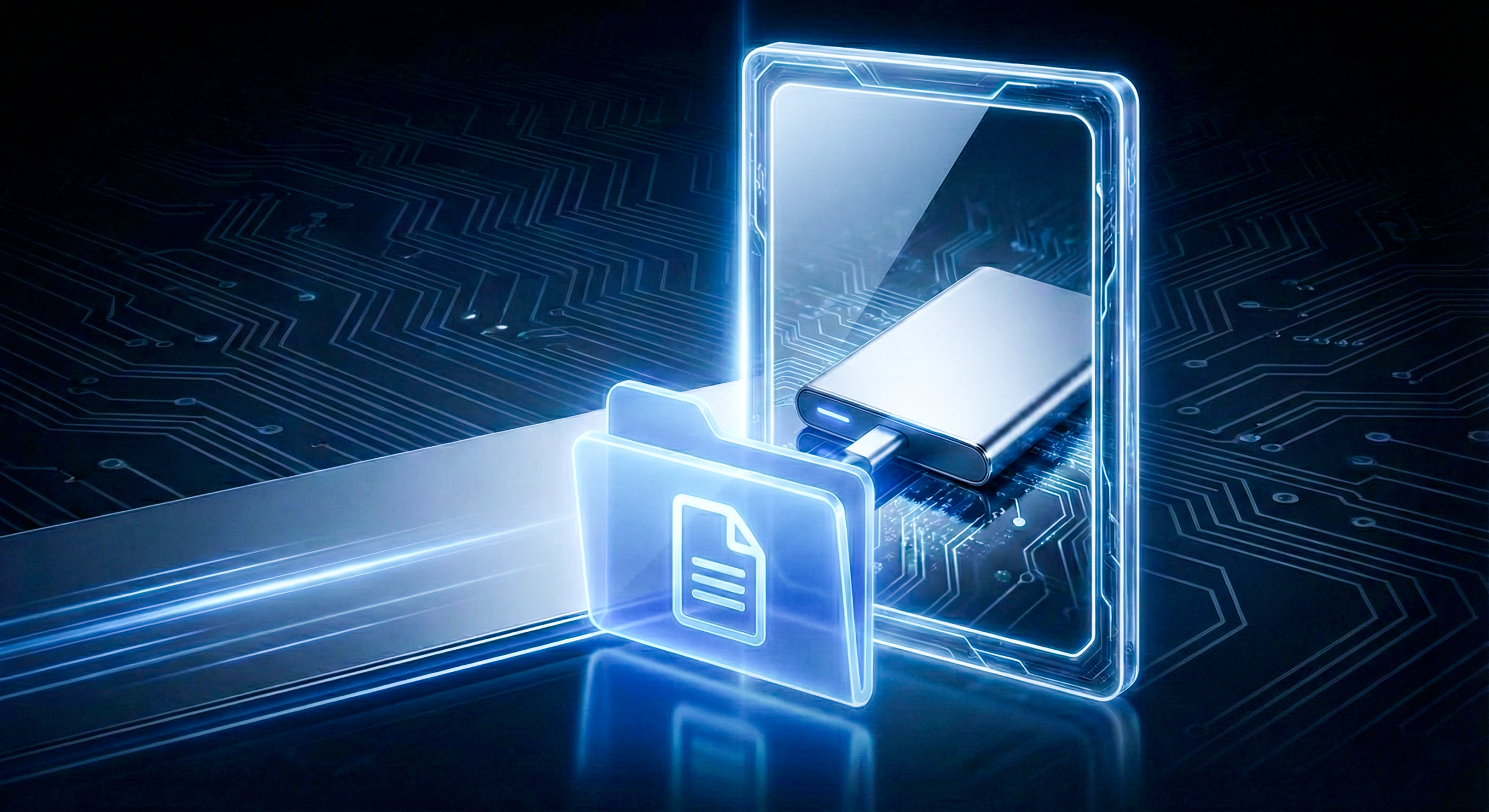
When you need to mirror folder mac data to an external drive, you are looking for an exact 1:1 replica, not a history of file versions like Time Machine provides. Perhaps you are a photographer backing up a shoot, or a developer saving a project state; you want the destination to look exactly like the source, meaning new files are added, modified files are updated, and—crucially—files deleted from the source are removed from the destination. We’ll look at two ways to create this “mirror” effect so you can secure your data with confidence.
Table of Contents
What Does “Mirroring” Actually Mean?
In file management terms, a standard “copy” usually merges folders. If you drag Folder A to your external drive, it adds new files but rarely deletes old ones that no longer exist on your Mac.
To mirror folder mac directories properly, the process must be a “One-Way Sync.” The software scans both locations and ensures the destination becomes a perfect reflection of the source. This is great for creating bootable backups or clean archives, but it requires caution: if you accidentally delete a file on your Mac and then run a mirror operation, that file will be deleted from your backup too.
How to mirror folder on Mac using Terminal?
macOS comes with a powerful Unix tool called rsync that is perfect for mirroring. It is fast and efficient because it only copies the specific bits of data that have changed. Launch Terminal from the Applications folder to begin.
To mirror a folder named “Projects” to an external drive named “BackupDrive”, type:
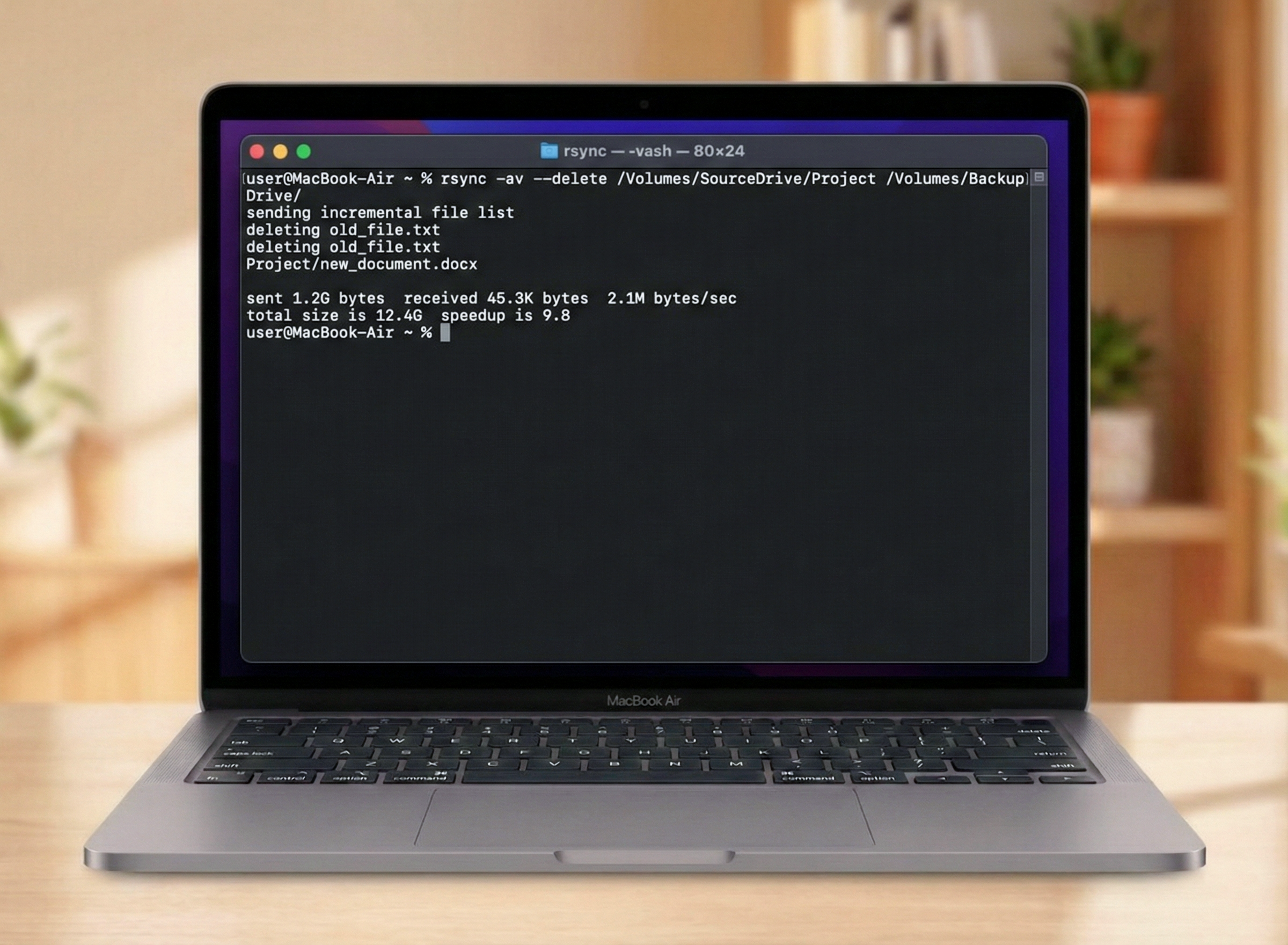
rsync -av --delete ~/Documents/Projects/ /Volumes/BackupDrive/Projects/
Breakdown of the command:
- -a: Archive mode (preserves permissions, dates, and times).
- -v: Verbose (shows you what files are being copied).
- –delete: This is the specific flag that tells the system to mirror folder mac behavior effectively by deleting files in the destination that are not in the source.
- Trailing slashes (/): These are critical in rsync. A slash at the end of the source path means “contents of this folder.”
Limitations:
One wrong character in the Terminal command can lead to data loss. If you get the path wrong with the –delete flag, you might wipe the wrong folder. It also lacks a “preview” mode to show you what will be deleted before you hit Enter.
How to mirror folder on Mac using DCommander?
A much easier and safer way to mirror folder mac data is to use DCommander. It features a dedicated Synchronize Folders tool that provides a visual interface for comparing folders. You can see exactly which files will be copied and, more importantly, which ones will be deleted, visualized with color codes before you commit to the action.
First, download and run DCommander.
- Set Up Panes: Open your source folder (e.g., Documents) in the Left pane and your destination (External Drive) in the Right pane.
- Open Sync Tool: Click the Synchronize button in the toolbar (or via the Tools menu).
- Configure: Check Scan folder contents (to include sub-folders) and check Left to Right one-way sync.
- Compare: Click the Compare button.
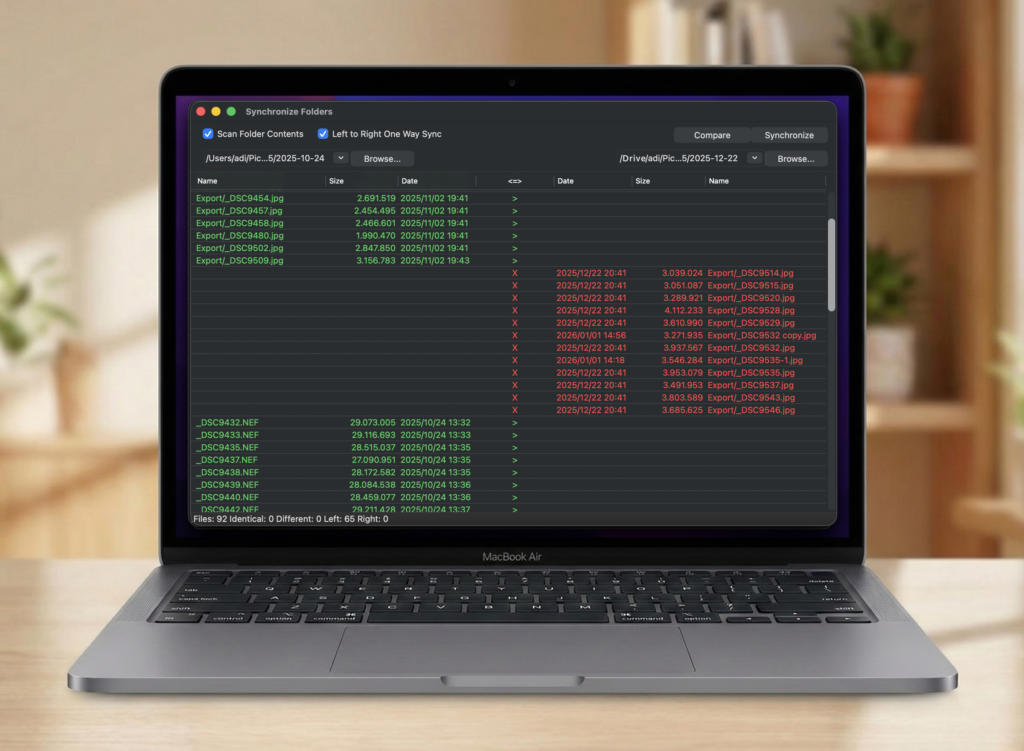
Why this is superior:
- Visual Confidence: You will see a list of actions.
- Green (>): Files copying from Mac to Drive.
- Red (X): Files that will be deleted from the Drive because they no longer exist on your Mac.
- Safety Check: If you see too many Red ‘X’s, you know something is wrong before you lose data.
- One-Click Execution: Once satisfied, click Synchronize to perform the mirror folder mac operation.
- Permissions Handling: DCommander handles system permissions gracefully, ensuring all metadata and dates are preserved on the backup.
Tips for Safe Mirroring
When you perform a mirror folder mac task, keep these safety tips in mind:
- Don’t Mirror to Time Machine: Never try to mirror a folder manually onto a drive that Time Machine is currently using. It can corrupt the Time Machine database.
- Verify Deletions: Always double-check the “Delete” list in DCommander’s preview. Did you really mean to delete those photos from the source?
- File Systems Matter: If you are mirroring to a USB stick formatted as FAT32 or ExFAT, some Mac-specific metadata (like color tags) might be lost. Using APFS or HFS+ on the external drive is best for a true mirror.
Conclusion
Mirroring is the definitive way to keep an external folder up to date with your current work. While the Terminal rsync command is a powerful industry standard, it offers zero forgiveness for typos. DCommander offers the same robust power but wraps it in a safety-first interface. By allowing you to visualize differences and confirm deletions, DCommander makes the mirror folder mac process stress-free and reliable.